Electric Charge
Electrostatics is the branch of science dealing with the static electricity i.e. electricity at rest
The knowledge of various laws which governs the behaviour of static electricity is essential. It is essential in the design and applications of insulation(particularly for high voltages). In the study of causes of lightning and protection against it and in the design and operation of transmission lines. Therefore, in this blog we shall briefly discuss some of the fundamental laws of electrostatics.
Electric charge possess two different forms first when it is static second when it is moving. Electric charge exhibits two different properties in two different forms when it is stable state and when it is moving. When it is moving it shows properties like Electric current, Magnetic effect,Heating effect, Electromagnetic Induction and so on.
Definitions:
Electrostatics: Electrostatics is the branch of electricity in which properties of static (non-moving) electric charges are studied. Or , Electrostatics is branch of physics which studies properties of electron at rest.
Concept:
There are two types of thing present in our nature one is matter and another one is radiation. Matter is something which has mass,momentum,volume,shape,kinetic energy etc. On the other hand Radiation is something which has wavelength, frequency (vibrations) etc. Matter is something on which we can apply force and on reaction matter also applies force.
So there are two root causes of forces in nature, 1) Gravitational Force 2) Electromagnetic Force
Reason behind the gravitational pull is mass. The gravity is totally dependent upon mass. As earth possess the gravitational pull because it contains mass. In a similar way reason behind the electromagnetic force is CHARGE. The charge itself is responsible for the electromagnetic force. Every particle in this universe possess charge in the form of static charge. We come to know when some body has charges or not, when we rub two bodies on one another it make charges uniform and unidirectional and that is how we can feel charge.
Modern Electron Theory
According to the modern theory, in an atom of an element, electrons (which are charges of negative electricity) revolve in orbits around the nucleus. In addition to the orbital motion, the electrons spin on their own axes, just as the earth spins around its axis. A spinning electron sets up the magnetic field along its axis of spin and the direction of field depends upon the direction of spin. When an atom do not possess charge then the electrons inside the atoms are in random motion. So the net charge is zero as the magnetic fields cuts each other. when we rub the body the the magnetic axes of the various domains are oriented so that they coincide with the direction of magnetomotive force. Thereby ultimately giving the strongest resultant magnetic field. So we called that body posses the charge.
Electric Charge:
According to the modern electron theory, normally every atom and therefore, every body consisting of a number of such atoms contains equal number of protons charged with positive electricity and electrons charged with negative electricity. Hence it is electrically neutral. But it is always possible to change the number of electrons in the body by adopting different methods. Then such a body with unequal number of electrons and protons is said to be electrically charged. When body contains more number of electrons than usual then it is called Negatively charged . On the other hand, a body that contains less than its normal number of electrons is said to be positively charged. The simplest method to change the number of electrons in a body so as to charge it is to rub it with a different material. For example, if a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk, free electrons from the glass rod move to the silk. Hence, there is deficiency of electrons in a glass rod and so it exhibits positive charge. The silk gets negatively charged due to excess of electrons in it.
Laws of Electrostatics.
- Like Charges Repel and Unlike Charges Attract Each Other: When two glass rods are rubbed with silk gets positively charges and if that two glass rods now has similar charge if brought closer to each other it repels one another. It is same with the two negatively charged bodies. Now if two bodies with opposite charges brought closer to each other then they attract each other.
- Coulombs Inverse Square Law: This law is based on the experimental results obtained by coulomb. Coulomb's Inverse Square Law states that the mechanical force (either due to attraction or repulsion) between two small charged bodies is : 1) Directly proportional to the product of charges 2) Inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them and 3) Depends upon the nature of the surrounding medium. Mathematical expression of law is: Force (F) = Q1Q2/ d^2
Facts about charge
- There are two types of charges present one is positive charge and another is negative charge.
- Charges experience the force of repulsion when two similar charges comes in contact or interacts with each other.
- On the other hand if two dissimilar charges interact with each other then there is force of attraction between both charges.
- In ordinary matter, electrons carries negative charge and protons carries positive charge in the nuclei of atoms.
- If there are equal number of positive charge and negative charge present then the positive and negative charges cancel each other and the net charge is zero.
- The charge on single electron is nearly about 1.602×10−19 coulombs.
- The derived unit of charge is Ampere-hour (Ah) by the formula, Total Charge (Q) = Current (I) * Time(t)
- Another unit of charge is coulomb.
Technical Terms
- The static electric charge has electric field and if the charge is moving then it possess magnetic field .
- The combination of electric and magnetic fields is called as Electromagnetic field.
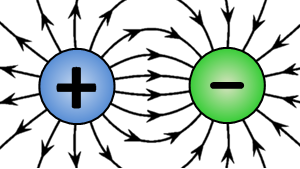
- When this field interacts with charges it gives rise to the electromagnetic force. for example if we took two charges one having positive charge and another having negative charge the there electric fields of two static charges interacts with each other and force of attraction develops between two charges.
- Ion (atoms or group of atoms) when looses its one or two electron develops a positive charge then the ion is called as cation or positively charged ion.
- On the other hand when ion gains one or two electrons then it develops net negative charge called as anion or negatively charged ion.
- Thus, deficiency or excess of electrons in a body can posses charge and it can be called as charged body.
- Charge is the fundamental property of forms of matter that exhibit electrostatic attraction or repulsion in the presence of other matter.

Summary
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charge: positive and negative (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively). Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with an absence of net charge is referred to as neutral.
For birth of electricity go here http://localhost/viralelectron/index.php/2020/05/13/dawn-of-electricity/
For Further reading refer: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_charge



Comments
Post a Comment